In today’s unpredictable financial landscape, risk management for long-term investors has become more crucial than ever. While the allure of high returns may tempt many to overlook potential downsides, seasoned investors know that protecting capital is equally important as growing it. Whether you’re saving for retirement, building generational wealth, or working toward other long-term financial goals, a robust risk management framework can be the difference between achieving your objectives and facing devastating setbacks.
Did you know that investors who implement comprehensive risk management strategies typically experience 40% less portfolio volatility during market downturns? This resilience not only preserves wealth but also provides peace of mind during turbulent economic periods.
This guide explores essential risk management techniques designed specifically for investors with time horizons of 10+ years, helping you build a fortress around your financial future while still capturing growth opportunities.
Understanding Investment Risk: Beyond Simple Volatility
Risk in investing extends far beyond simple market fluctuations. For long-term investors, understanding the multidimensional nature of risk is the foundation of effective investment risk diversification.
Different Types of Investment Risks
Market Risk: Also known as systematic risk, this affects entire markets and cannot be eliminated through diversification alone. Examples include recessions, interest rate changes, and geopolitical events.
Inflation Risk: The silent wealth eroder that gradually diminishes purchasing power over time—particularly dangerous for long-term investors relying on fixed-income investments.
Longevity Risk: The possibility of outliving your savings, a growing concern as global life expectancies increase.
Concentration Risk: The danger of having too many eggs in one basket, whether in a single company, sector, or geographic region.
Liquidity Risk: The inability to convert investments to cash without significant loss of value when needed.
Sequence of Returns Risk: Particularly relevant for retirees, this refers to the potentially devastating impact of experiencing poor market returns in early retirement years.
Risk Tolerance Assessment
Before implementing any portfolio protection strategies, it’s essential to understand your personal risk tolerance. This psychological factor varies widely between individuals and is influenced by:
- Financial goals and time horizon
- Income stability and emergency reserves
- Personal comfort with volatility
- Family circumstances and obligations
- Overall financial knowledge
Risk management for long-term investors involves systematically identifying potential threats to investment goals, quantifying their potential impact, and implementing strategies to mitigate them while maintaining progress toward financial objectives. Effective risk management doesn’t eliminate risk but transforms unpredictable dangers into calculated decisions.
Essential Risk Management Strategies for Long-Term Success
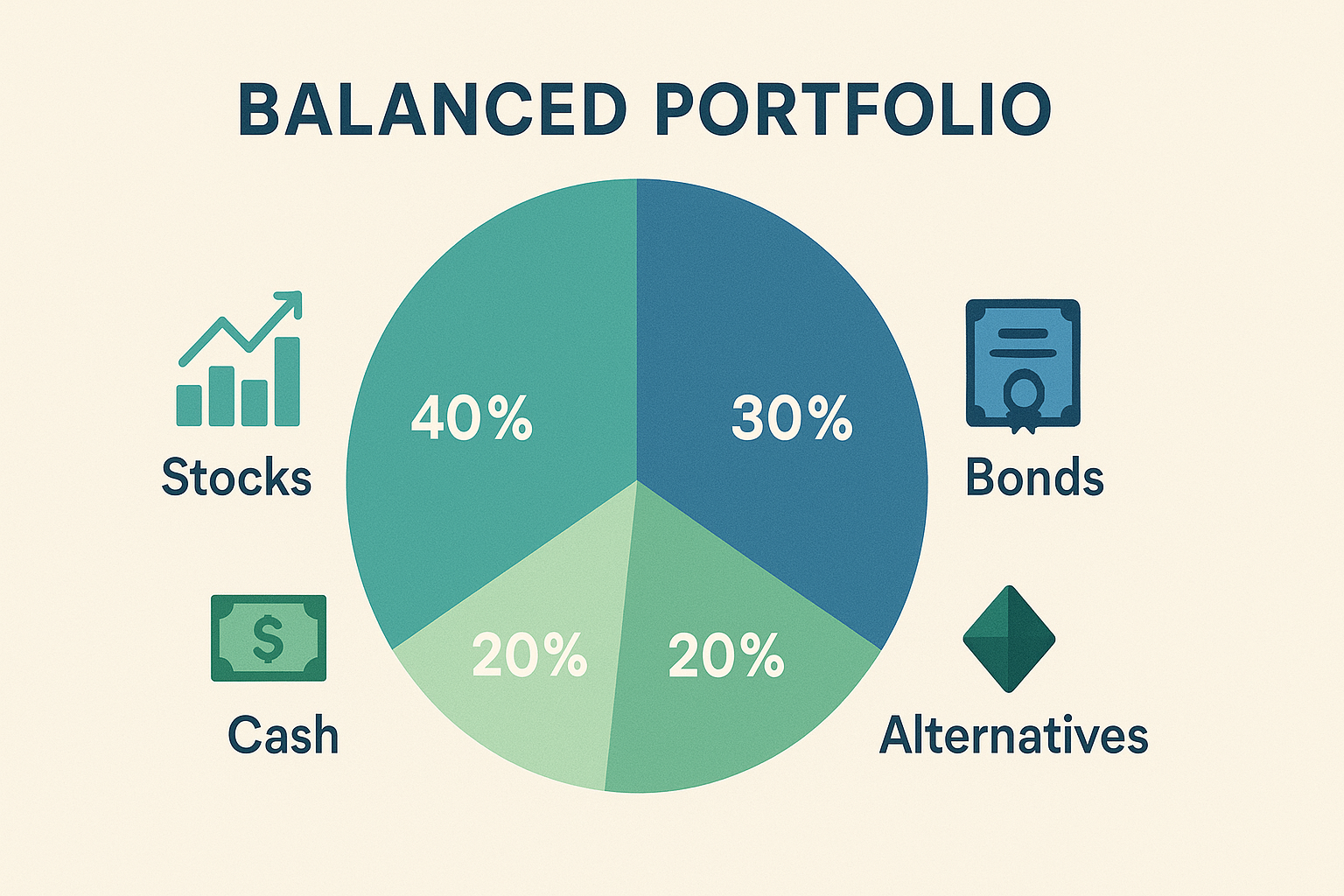
1. Strategic Asset Allocation
The cornerstone of long-term investment security is thoughtful asset allocation—distributing investments across various asset classes to balance risk and return potential. Research consistently shows that asset allocation determines approximately 90% of portfolio performance variability.
A well-designed allocation should consider:
- Your time horizon (when you’ll need the money)
- Risk tolerance (both emotional and financial)
- Income requirements
- Tax situation
- Economic outlook
Example of Strategic Asset Allocation for Different Age Groups:
Age GroupStocksBondsAlternativesCash20s-30s80-90%5-15%0-10%0-5%40s-50s60-80%15-30%5-15%5-10%60s+40-60%25-45%5-15%5-15%
Note: These are general guidelines; individual allocations should be personalized based on specific circumstances.
2. Diversification: The Investor’s Ultimate Defense
While asset allocation divides investments between major categories, diversification refines this approach by spreading investments within each category. Proper investment risk diversification includes:
- Geographic diversification: Domestic and international markets
- Sector diversification: Exposure across different industries
- Style diversification: Growth and value investments
- Size diversification: Large, mid, and small-cap companies
- Security-type diversification: Individual securities, funds, ETFs
Modern portfolio theory suggests that combining assets with low correlation can significantly reduce portfolio volatility without necessarily sacrificing returns.
3. Tactical Rebalancing for Risk Control
Even with ideal initial allocation, market movements will gradually skew your portfolio away from target percentages. Consistent rebalancing is a crucial aspect of market volatility management that:
- Forces disciplined buying low and selling high
- Maintains intended risk levels
- Minimizes emotional decision-making
- Potentially increases returns while decreasing volatility
Rebalancing Approaches:
- Calendar rebalancing: Adjusting at set intervals (quarterly, semi-annually, annually)
- Threshold rebalancing: Realigning when allocations drift beyond predetermined percentages
- Hybrid methods: Combining calendar and threshold approaches
Research from Vanguard suggests that rebalancing when allocations drift by 5% or more from targets strikes an effective balance between risk management and transaction costs.
4. Strategic Use of Hedging Tools
For sophisticated investors, hedging instruments can provide additional layers of portfolio protection strategies during periods of expected turbulence:
- Options strategies: Using puts for downside protection or covered calls for income
- Inverse ETFs: Providing temporary protection against specific market declines
- Stop-loss orders: Automating exits at predetermined price points
While these tools require more advanced knowledge, they can be valuable components of a comprehensive risk management approach.
Advanced Risk Management Considerations for Different Life Stages
Risk Management for Wealth Accumulation Phase
During early and mid-career stages, investors should focus on:
- Dollar-cost averaging: Systematically investing regardless of market conditions
- Higher growth allocation: Accepting greater volatility for long-term return potential
- Human capital considerations: Aligning investment risk with career stability
- Extended time horizon benefits: Using time to recover from market corrections
Risk Management Near and During Retirement
As retirement approaches and during the distribution phase, retirement risk planning becomes paramount:
- Liability-matching strategies: Aligning certain investments with anticipated expenses
- Bucket approaches: Segmenting portfolios by time horizon
- Withdrawal rate management: Implementing sustainable distribution strategies
- Longevity protection: Considering partial annuitization or other guaranteed income sources
Research from Trinity University suggests maintaining a 50-60% equity allocation even during retirement can provide the optimal balance between growth potential and withdrawal sustainability.
Psychological Aspects of Risk Management
The greatest risk management plan is worthless if emotional reactions derail it during market stress. Successful long-term investment security requires addressing psychological factors:
Behavioral Biases to Guard Against
- Loss aversion: The tendency to feel losses more powerfully than equivalent gains
- Recency bias: Overweighting recent events when making decisions
- Herd mentality: Following the crowd rather than adhering to strategy
- Confirmation bias: Seeking information that reinforces existing beliefs
Implementing Psychological Safety Nets
- Written investment policy statements: Creating detailed guidelines before emotional situations arise
- Automated processes: Removing human emotion from regular investment activities
- Financial advisor partnerships: Adding an objective third-party perspective
- Education and preparation: Understanding market history to contextualize volatility
Technology and Tools for Modern Risk Management
Today’s investors have unprecedented access to sophisticated risk assessment and management tools:
- Risk analysis platforms: Software that quantifies portfolio risk exposures
- Scenario testing: Stress-testing portfolios against historical and hypothetical market conditions
- Automated rebalancing services: Technology that maintains risk parameters with minimal intervention
- Goal-based planning tools: Applications linking investment strategies directly to life objectives
These technological advances make professional-grade market volatility management accessible even to individual investors.
Creating Your Personalized Risk Management Plan
Effective risk management must be tailored to individual circumstances. Follow these steps to develop your personalized framework:
- Define clear financial objectives with specific time horizons
- Assess your true risk tolerance using both questionnaires and reflection
- Identify specific risks most relevant to your situation
- Develop mitigation strategies for each identified risk
- Implement protective mechanisms appropriate for your knowledge level
- Schedule regular reviews to assess and adjust as needed
Remember that risk management isn’t about eliminating risk but transforming unpredictable dangers into calculated decisions aligned with your long-term goals.
Conclusion: The Long-Term Advantage of Strategic Risk Management
Mastering risk management for long-term investors doesn’t happen overnight, but the cumulative benefits of deliberate risk planning compound over time. By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, you’re not just protecting against downside—you’re creating a resilient framework that can weather various market conditions while maintaining progress toward your most important financial goals.
The most successful investors understand that true wealth-building isn’t about chasing the highest returns but about consistent progress with thoughtful protection. Start implementing these risk management principles today, and you’ll likely find yourself making more confident decisions with greater peace of mind regardless of market conditions.
If you’re a Cautious investor, our quiz can help confirm your strategy.
Other Investors Read;
Technical Analysis for Long-Term Investors: A Comprehensive Guide
How to Build a Dividend Growth Portfolio
Building a Balanced Investment Portfolio: A Complete Guide to Financial Diversification